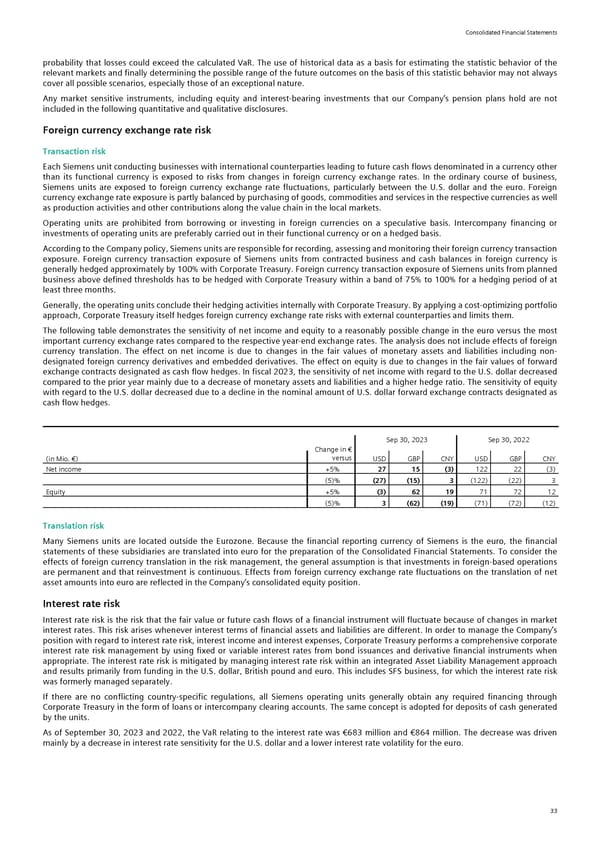
Consolidated Financial Statements probability that losses could exceed the calculated VaR. The use of historical data as a basis for estimating the statistic behavior of the relevant markets and finally determining the possible range of the future outcomes on the basis of this statistic behavior may not always cover all possible scenarios, especially those of an exceptional nature. Any market sensitive instruments, including equity and interest-bearing investments that our Company’s pension plans hold are not included in the following quantitative and qualitative disclosures. Foreign currency exchange rate risk Transaction risk Each Siemens unit conducting businesses with international counterparties leading to future cash flows denominated in a currency other than its functional currency is exposed to risks from changes in foreign currency exchange rates. In the ordinary course of business, Siemens units are exposed to foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations, particularly between the U.S. dollar and the euro. Foreign currency exchange rate exposure is partly balanced by purchasing of goods, commodities and services in the respective currencies as well as production activities and other contributions along the value chain in the local markets. Operating units are prohibited from borrowing or investing in foreign currencies on a speculative basis. Intercompany financing or investments of operating units are preferably carried out in their functional currency or on a hedged basis. According to the Company policy, Siemens units are responsible for recording, assessing and monitoring their foreign currency transaction exposure. Foreign currency transaction exposure of Siemens units from contracted business and cash balances in foreign currency is generally hedged approximately by 100% with Corporate Treasury. Foreign currency transaction exposure of Siemens units from planned business above defined thresholds has to be hedged with Corporate Treasury within a band of 75% to 100% for a hedging period of at least three months. Generally, the operating units conclude their hedging activities internally with Corporate Treasury. By applying a cost-optimizing portfolio approach, Corporate Treasury itself hedges foreign currency exchange rate risks with external counterparties and limits them. The following table demonstrates the sensitivity of net income and equity to a reasonably possible change in the euro versus the most important currency exchange rates compared to the respective year-end exchange rates. The analysis does not include effects of foreign currency translation. The effect on net income is due to changes in the fair values of monetary assets and liabilities including non- designated foreign currency derivatives and embedded derivatives. The effect on equity is due to changes in the fair values of forward exchange contracts designated as cash flow hedges. In fiscal 2023, the sensitivity of net income with regard to the U.S. dollar decreased compared to the prior year mainly due to a decrease of monetary assets and liabilities and a higher hedge ratio. The sensitivity of equity with regard to the U.S. dollar decreased due to a decline in the nominal amount of U.S. dollar forward exchange contracts designated as cash flow hedges. Sep 30, 2023 Sep 30, 2022 Change in € versus (in Mio. €) USD GBP CNY USD GBP CNY Net income +5% 27 15 (3) 122 22 (3) (5)% (27) (15) 3 (122) (22) 3 Equity +5% (3) 62 19 71 72 12 (5)% 3 (62) (19) (71) (72) (12) Translation risk Many Siemens units are located outside the Eurozone. Because the financial reporting currency of Siemens is the euro, the financial statements of these subsidiaries are translated into euro for the preparation of the Consolidated Financial Statements. To consider the effects of foreign currency translation in the risk management, the general assumption is that investments in foreign-based operations are permanent and that reinvestment is continuous. Effects from foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations on the translation of net asset amounts into euro are reflected in the Company’s consolidated equity position. Interest rate risk Interest rate risk is the risk that the fair value or future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate because of changes in market interest rates. This risk arises whenever interest terms of financial assets and liabilities are different. In order to manage the Company’s position with regard to interest rate risk, interest income and interest expenses, Corporate Treasury performs a comprehensive corporate interest rate risk management by using fixed or variable interest rates from bond issuances and derivative financial instruments when appropriate. The interest rate risk is mitigated by managing interest rate risk within an integrated Asset Liability Management approach and results primarily from funding in the U.S. dollar, British pound and euro. This includes SFS business, for which the interest rate risk was formerly managed separately. If there are no conflicting country-specific regulations, all Siemens operating units generally obtain any required financing through Corporate Treasury in the form of loans or intercompany clearing accounts. The same concept is adopted for deposits of cash generated by the units. As of September 30, 2023 and 2022, the VaR relating to the interest rate was €683 million and €864 million. The decrease was driven mainly by a decrease in interest rate sensitivity for the U.S. dollar and a lower interest rate volatility for the euro. 33
 Siemens Report FY2023 Page 78 Page 80
Siemens Report FY2023 Page 78 Page 80